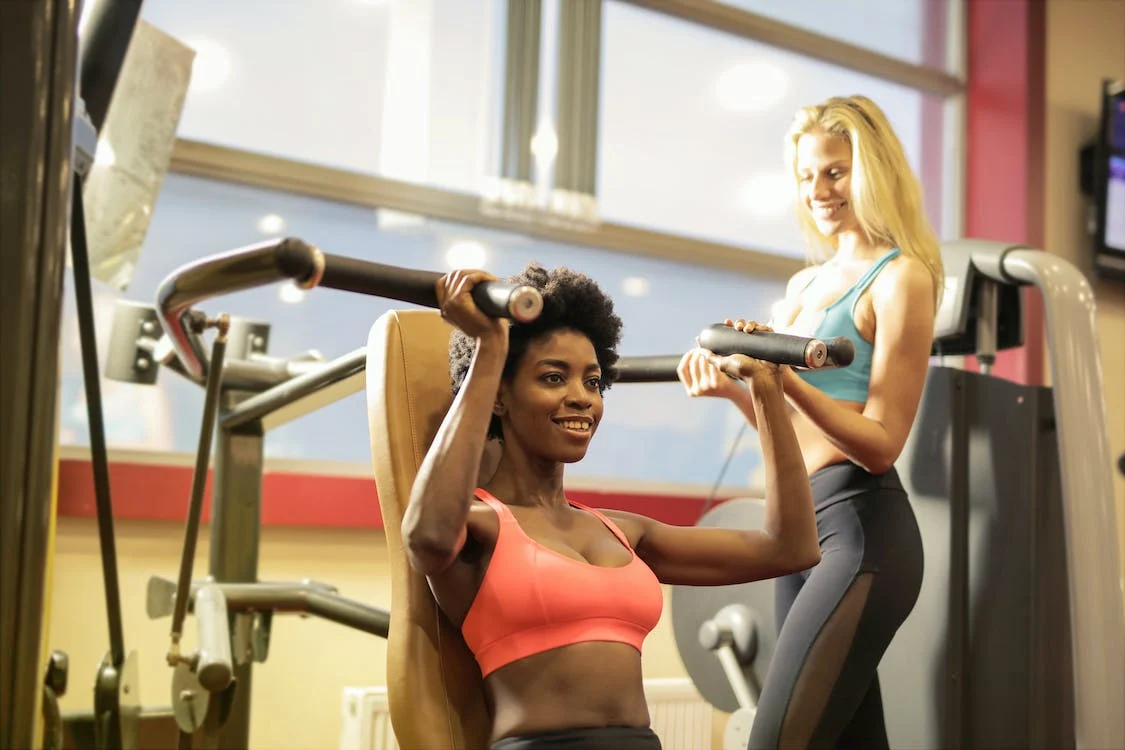After reviewing over 200 research on the benefits of resistance training (commonly known as strength training) on muscular strength and mass. According to the authors, both were shown to be improved by this kind of exercise, independent of intensity or frequency of sessions.
Examining Weight, Reps, and Frequency
Research has been delayed regarding the effects of strength training compared to aerobic exercise. Often, advice provided by fitness professionals is based on traditional guidelines developed for athletic training, which may not always apply to the general population.
Nevertheless, with the accumulated data on resistance training and weightlifting, researchers felt the need to establish a more specific guideline for it. To do this, they examined 192 past studies that looked into the effects of various resistance exercises on over 5,000 healthy adults. The studies revealed that different resistance training methods, whether using heavy or light weights, performing one to three sets, or exercising once to three times a week, all increased strength and muscle building.
Furthermore, it was observed that using heavier weights resulted in greater strength gains, and performing multiple sets increased muscle mass. The main takeaway from the research was that to engage in resistance training regularly, even more so than trying to perfect the approach.
While it's evident that some exercise is better than none, healthcare providers need to continue endorsing current guidelines on muscle-strengthening activities. These suggest that healthy adults should engage in such workouts at least twice a week. Simultaneously, the research on weightlifting indicates the benefits of resistance training even if done less frequently than these often-cited recommendations.
5 Simple and Effective Training Regimes

Here are five tried-and-true methods that have worked for athletes in the past and might serve as a basis for your own strength training regimen.
Strength training
Bodybuilding is a resistance exercise that aims to muscle building and alter overall body composition. Because of this, it is often used for purely cosmetic reasons by sportsmen. The appearance and size of your muscles are emphasized.
Programming for a bodybuilder will include a limitless variety of workouts. Both complex workouts and accessory work are essential to the bodybuilding process. Multi-joint or multi-muscle movements are known as compound exercises. Compound motions include the squat, the deadlift, and the bench press, among others. Isolating more precise regions is useful while working on add-ons. Isolated muscle groups may be worked out more effectively using exercises like pull-ups, curls, and planks.
Lighter weights and more repetitions (about 8-12) with less rest in between sets characterize the majority of bodybuilding and hypertrophy workouts. This strategy is beneficial since it helps you build up more glycogen and enzymes as muscle fuel. This is the main factor in developing larger muscles.
Brute Strength Powerlifting
Consider the powerlifter's ultimate objective: to move the most weight possible. That's why competitions testing absolute strength are held. To achieve this goal, going heavy is essential.
The weights you lift will be much heavier than in bodybuilding, and the number of repetitions you complete will be much lower (between 3 and 8).
You may apply this idea to your squats, deadlifts, and dumbbell presses at the gym. The key is progressive overload, gradually increasing your weight over time. In this manner, you put your muscles to the test on a regular basis, which is when they expand.
Why is powerlifting so effective at muscle building? You'll have better nerve and muscle function and be able to lift more weight. Your body needs to adapt to a new level of challenge if you want to squat 300 pounds. This explains why powerlifters do fewer repetitions with much heavier weights.
Circuit training
During circuit training, you'll do five to ten exercises in a row or a "circuit." You can perform this for a certain period or number of rounds. Circuits consist of consecutive exercise sets separated by brief periods of relaxation. Dumbbell squats, push-ups, sit-ups, curls, and lunges, for instance, may be performed in a 30-second circuit. After the two-minute break, repeat the process twice more.
The complete body may be challenged in a short period with circuit training. Although most circuit training programs use lower-weight (or even bodyweight) and higher-repetition exercises, you may modify them to suit your needs. Circuit training may be performed with almost any physical activity.
The Isometric Training
Static training is another name for isometric exercise. During this interval, the muscles (or muscles) contract but do not cause forward motion. What this means is that you are in a designated role. A wall sit is an example of an isometric exercise. Any isometric exercise may be made more difficult by the addition of weight. Put a plate on your back, do a push-up until your chest is an inch off the ground, and maintain that posture.
Isometric weight training has a simple but potent benefit: It's a simple approach to lengthen the period while tension is present. Muscles need time under strain to be torn down and rebuilt stronger than before.
However, it's worth noting that out of the five primary forms of weight training, the benefits from isometric work are much below those of the other ways. As a low-impact type of exercise, though, this is fantastic to integrate. Isometric exercise may be helpful if you're nursing an injury, dealing with joint pain, or just taking a day to actively rest.
High-intensity Interval Training
Training at a high volume needs no explanation. The weight must be lowered because of the increase in sets and repetitions. If you normally do squats with a moderate weight (say, 150 pounds), you may drop to 120 pounds and complete three sets of ten reps instead.
Adding more time under strain will lead to muscle growth, so keep racking up those repetitions. Incorporating progressive overload into weight training is also important. You'll notice that you can do more repetitions with the same weight as your strength increases, or vice versa.